How Drive Time is Calculated
An explanation of how eSpatial estimates Drive Time values and how to improve results.
Overview
Drive-time calculations are an estimate of how far you can travel from a center point in X minutes or time. The Drive-Time functionality produces an isochrone to represent the drive time coverage. An isochrone is a polygon made up of lines joining up sample points so by its nature is an estimated representation.
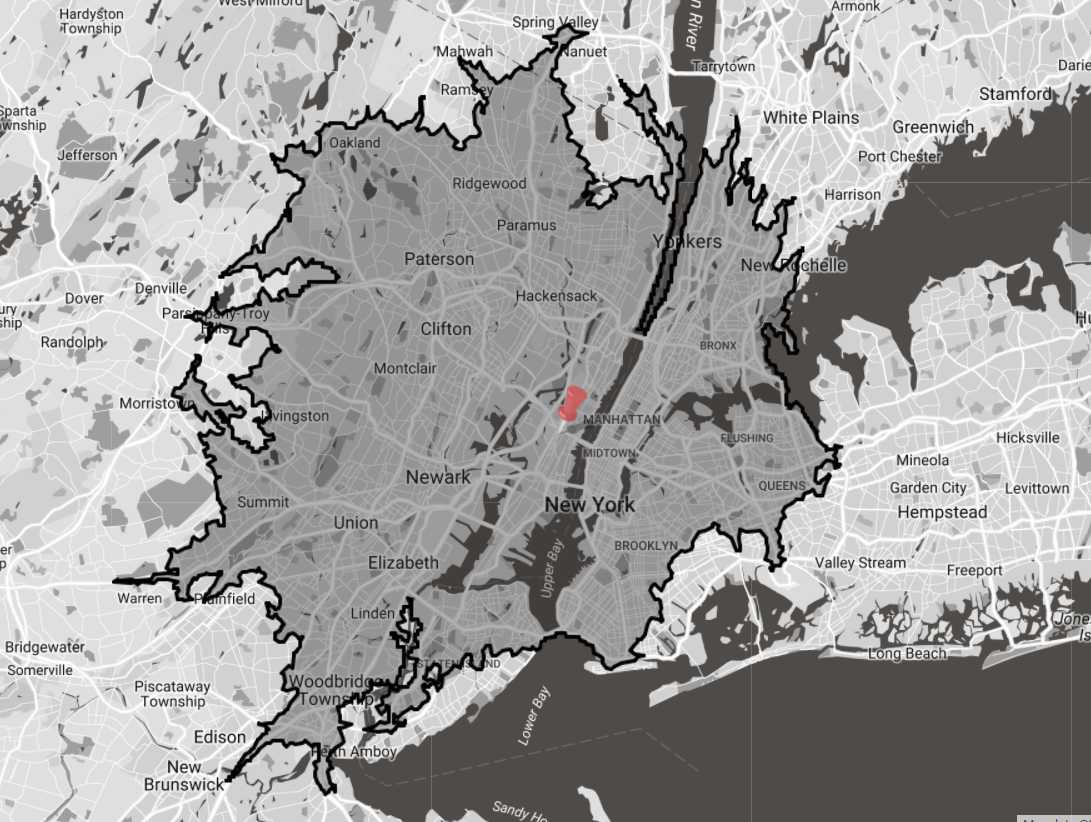
How it works
eSpatial uses Valhalla, the open source routing engine that is built on Open Street Maps data. The distance is calculated based on average car drive time which takes maximum road speed with road type adjustments into consideration. You can find additional details on the underlying data used to produce the drive-times here:
Within Drive-time Considerations
Drive-time buffers (isochrones) are estimates and are built on sample points.
You may find that some routing results that return a drive time greater than the buffer are inside the buffer and that some points that have a greater drive time than the buffer are located within the buffer. There are two main reasons for this:
- The drive time buffer is produced on estimates and a limited number of sample points.
- The drive-time buffers are built using the open-source Valhalla library that is built on Open Street Maps data. The routing is calculated using the Azure Maps API. They are both built on different underlying data and on different algorithms so there will be some differences in the results.
Related to the above, if you filter data in or out based on the within-drivetime buffer, you may remove data that you would not expect. This is due to the sample nature of the isochrone. It may also be due to one-way streets or similar.
The isochrone may not match up with the road network on the basemap. This is due to the sample nature of an isochrone and that the underlying data between open street maps and azure maps may differ.
Troubleshooting Drive Time Results
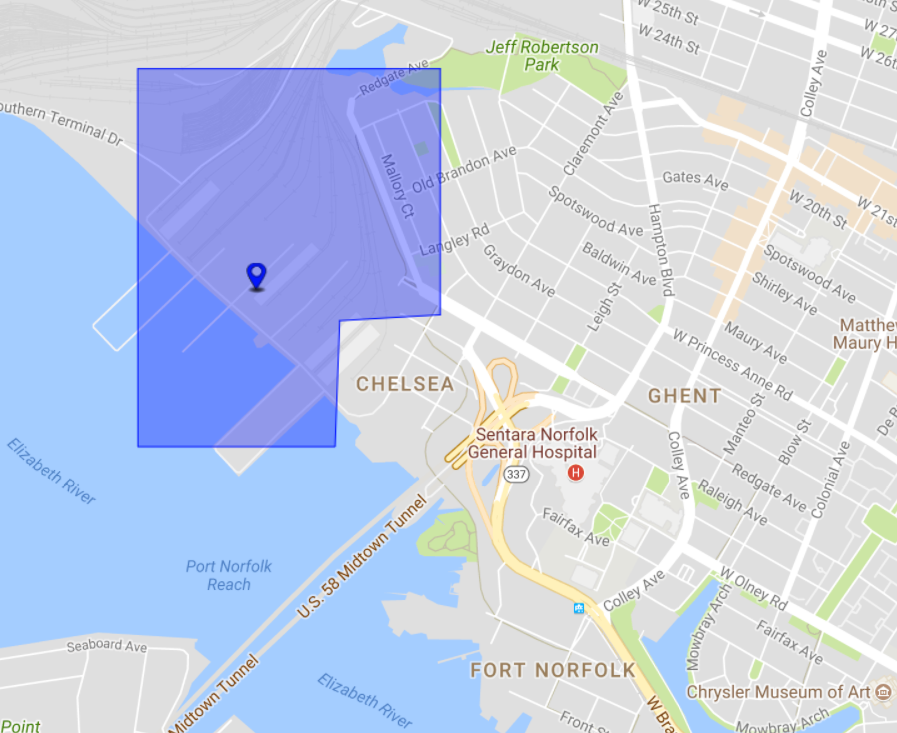
In areas with incomplete road network data, you may see similar results to the below. This is more likely to appear in rural areas. Including more detailed address information such as street name can normally address this. By moving the point closer to the road network can also help. When this occurs, they can be identified visually as they usually appear as a rectangle.
In this example, zip code is the highest level of accuracy. The point is located in a port/railway station so the road network is limited.
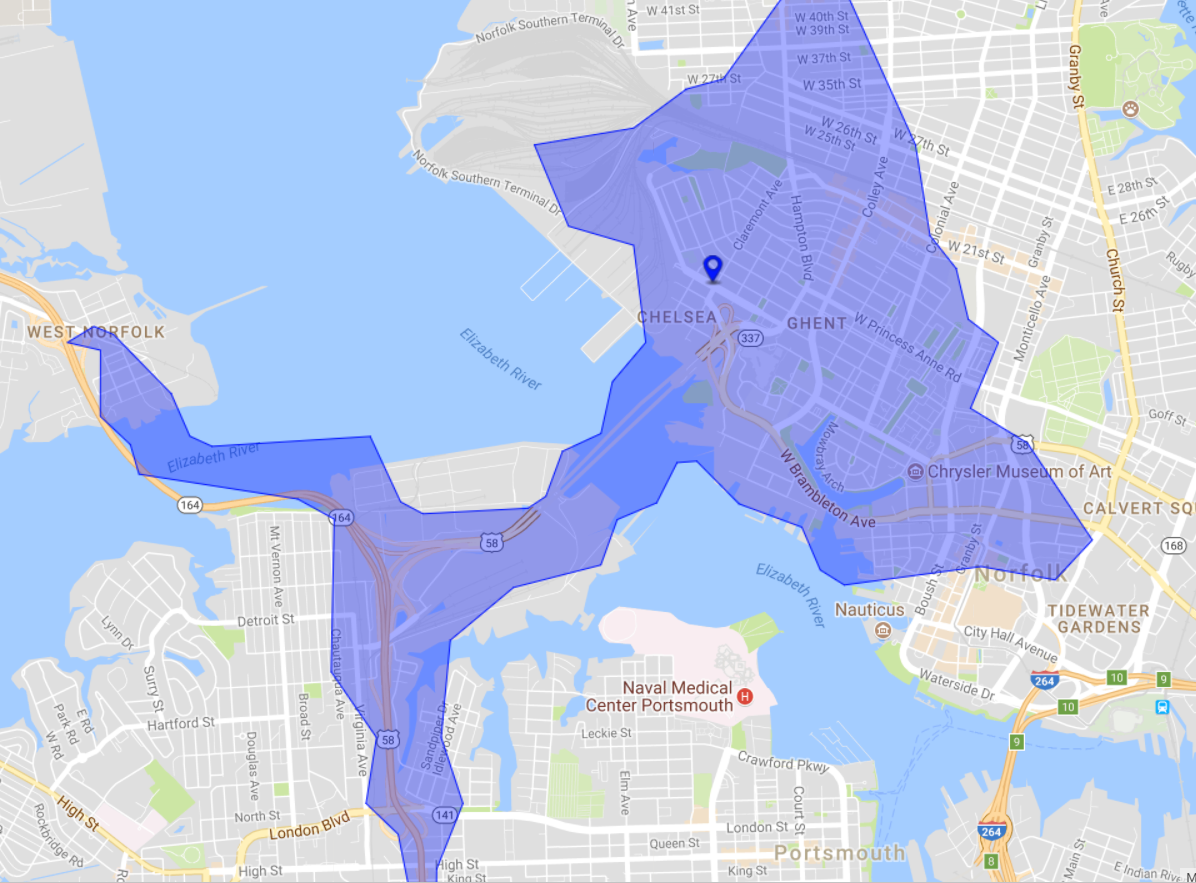
By moving the point onto the road network, the results are far better
Attribution
The open source Valhalla API used by eSpatial to create drive-times is built on OpenStreetMap. We acknowledge the contribution made to the community by © OpenStreetMap contributors.
